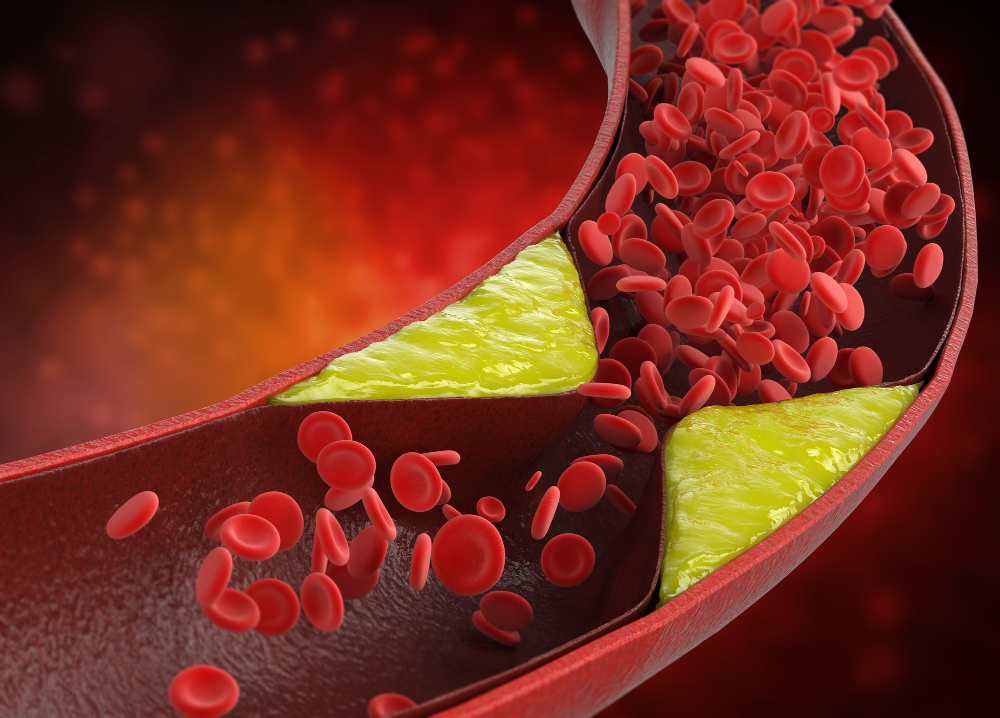
Heart disease is one of the leading causes of death worldwide, and high cholesterol is a significant risk factor for its development. Cholesterol is a waxy, fatty substance found in every cell of the body. However, when cholesterol levels in the blood are too high, it can build up in the arteries and form plaques that obstruct blood flow to the heart. In this article, we will explore the connection between cholesterol and heart disease, as well as strategies for maintaining a healthy heart.
- Cholesterol: LDL and HDL: Cholesterol is transported in the blood in two main forms: low-density lipoprotein (LDL) and high-density lipoprotein (HDL). LDL is commonly referred to as “bad cholesterol” as it can accumulate in the arteries and contribute to plaque development. On the other hand, HDL is considered “good cholesterol” as it helps remove excess cholesterol from the arteries and transports it back to the liver for disposal.
- Risk of Heart Disease: High cholesterol, especially elevated levels of LDL, increases the risk of heart disease. Plaques formed by excess cholesterol can narrow the coronary arteries, limiting blood flow to the heart and potentially leading to angina, heart attack, or stroke. Other risk factors such as high blood pressure, smoking, and diabetes can further exacerbate the impact of high cholesterol on cardiovascular health.
- Strategies for Maintaining a Healthy Heart:
- Healthy diet: Follow a balanced, low in saturated fats and cholesterol diet. Prioritize foods rich in fiber, fruits and vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins. Limit the consumption of processed, fried, and high-fat foods.
- Regular physical activity: Maintain an active lifestyle and engage in regular exercise. Aerobic exercises such as walking, running, swimming, or cycling can help improve cholesterol levels, strengthen the heart, and promote healthy blood circulation.
- Weight control: Maintain a healthy weight through a combination of proper nutrition and regular physical activity. Excess weight can increase cholesterol levels and the risk of heart disease.
- Smoking cessation: If you smoke, seek help to quit smoking. Smoking not only increases the risk of heart disease but also lowers HDL cholesterol levels, further worsening the lipid profile.
- Regular medical check-ups: Undergo regular medical check-ups and monitor your cholesterol levels. If you have a family history of heart disease or risk factors, it is important to monitor and treat any abnormalities in cholesterol levels.
High cholesterol and heart disease are closely linked. Maintaining healthy cholesterol levels, particularly by reducing LDL levels and increasing HDL levels, is crucial for protecting cardiovascular health. Adopting a healthy lifestyle that includes a balanced diet, regular physical activity, weight control, smoking cessation, and proper medical follow-up are key steps to maintaining a healthy heart. Remember that care and prevention are essential in reducing the risk of heart disease and promoting a fulfilling and healthy life.